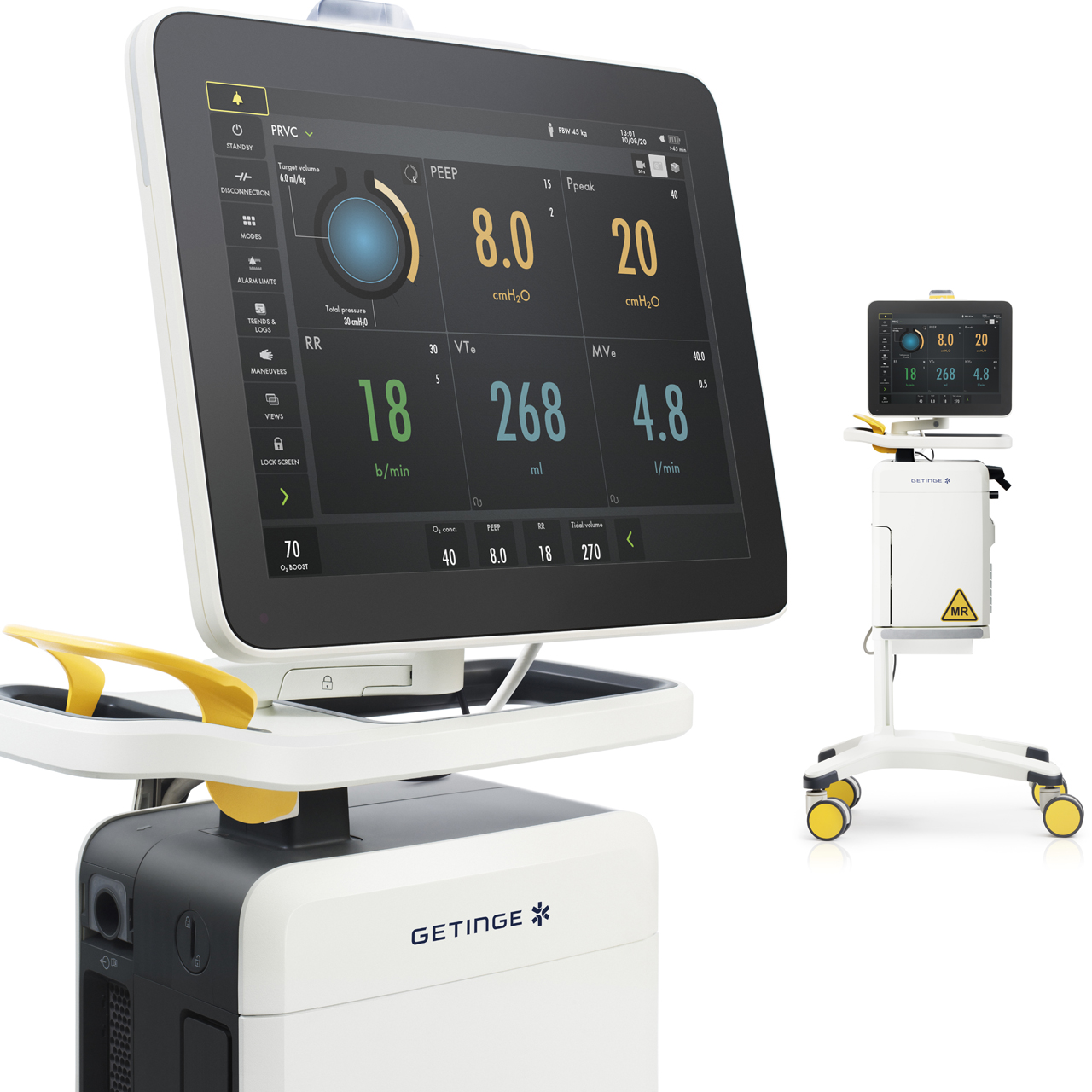
Built around your needs
Naturally, the ventilator itself is just one part of the equation. Our well-developed clinical and support organization backed the first MR Conditional Servo Ventilator more than 25 years ago and has been part of product development ever since.
Same experience, same settings
Servo-u MR is an effective complement to other ventilators in the Servo family. The common interface saves training time and eases patient transitions.
Servo-u and Servo-u MR also shares ventilation performance. This means that set and measured values are the same on both ventilators, making the transition of settings less complicated.
Related products
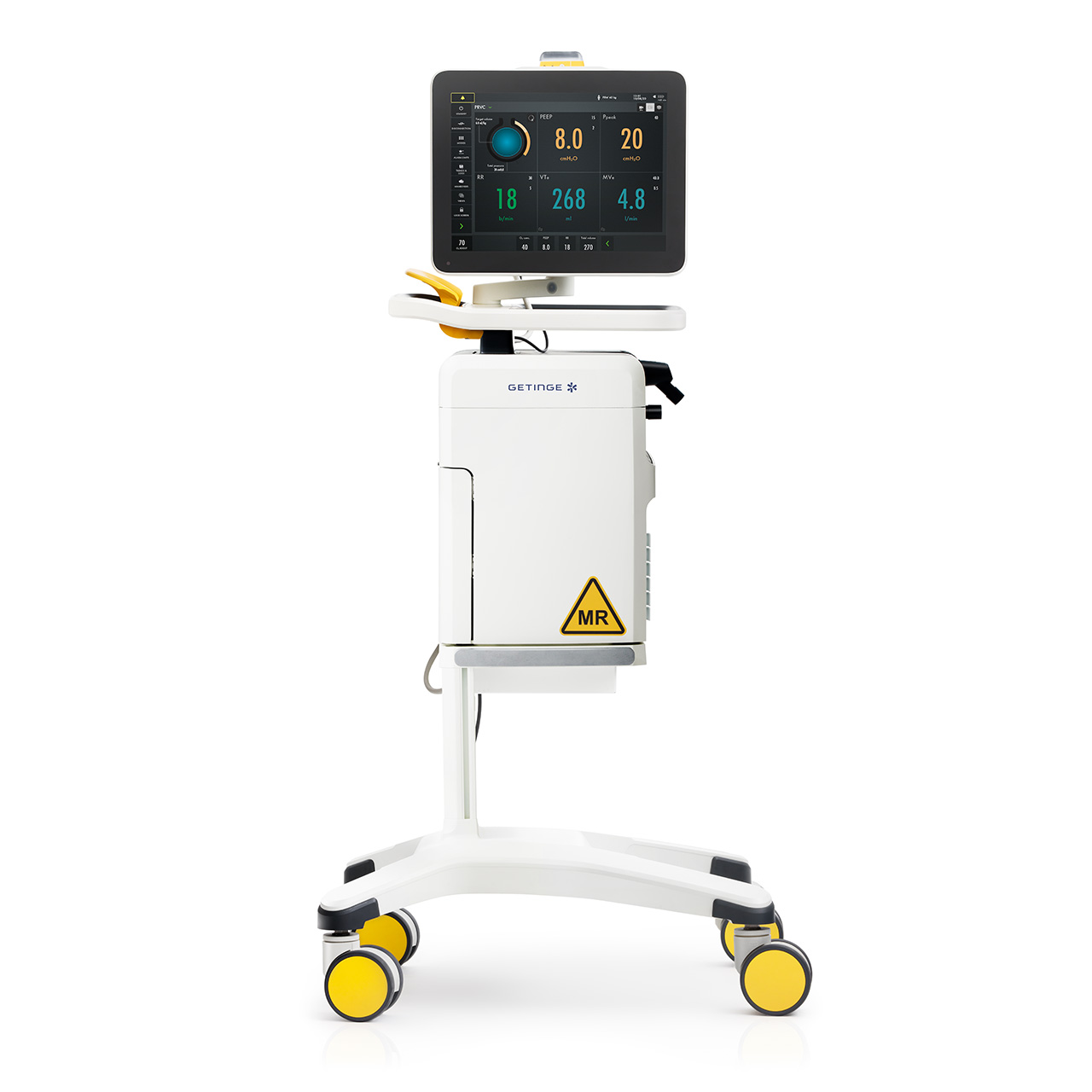
Safe positioning
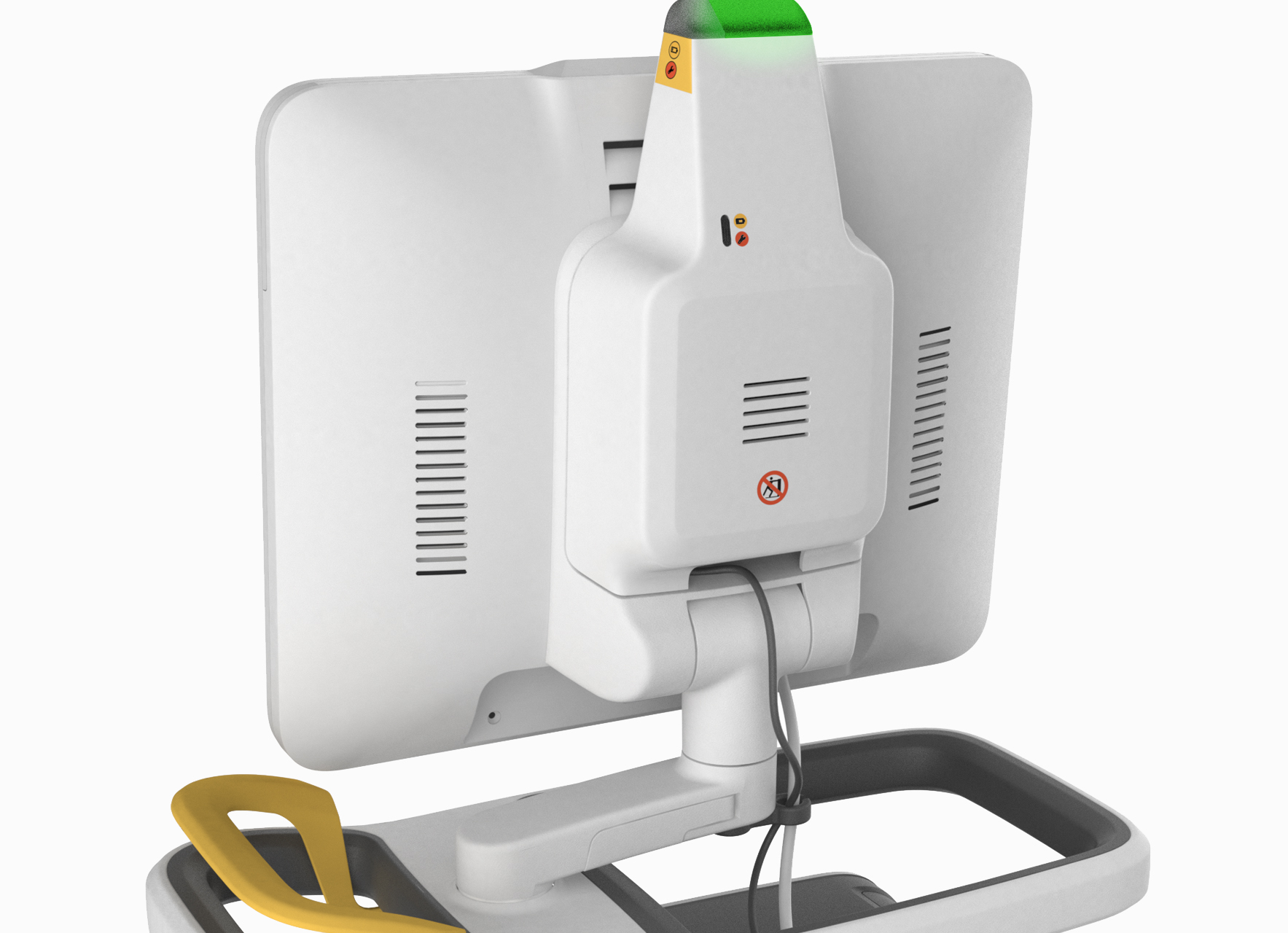
The magnetic field indicator guides you to a safe position, with visual and audible alerts. The auto-lock handle locks all wheels once your hand leaves the ventilator and the screen turns 360 degrees for flexible placement.
For all patients
Servo-u MR supports all patient categories, including neonates. Capabilities range from invasive and non-invasive ventilation to High Flow therapy, and the system comes with a range of defined accessories and consumables.
Protecting the lungs
The distance view lets you see vital parameters at a glance from the control room, and Servo Compass helps you sustain protective ventilation within set targets.
Securing your investment
Our well-developed clinical and support organization backed one of the first MR ventilators more than 25 years ago. We are on hand close to you, serving and providing resources for more than 100 000 Servo ventilators worldwide.
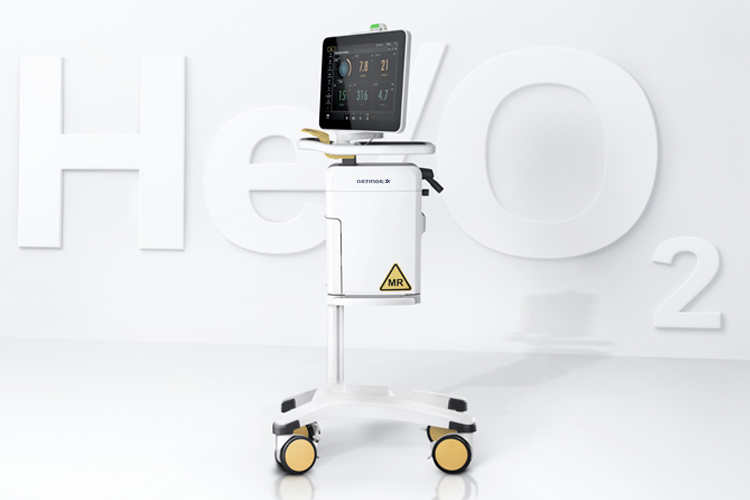

Heliox therapy in the MR room
The Servo-u MR is specifically designed with the radiological needs and requirements of the MR room in mind. To enable MR imaging of patients with various types of respiratory diseases, including those with severe airway obstruction, we have added Heliox therapy – a mixture of Helium and Oxygen that facilitates laminar flow and minimizes airway pressure due to its low density.[3]
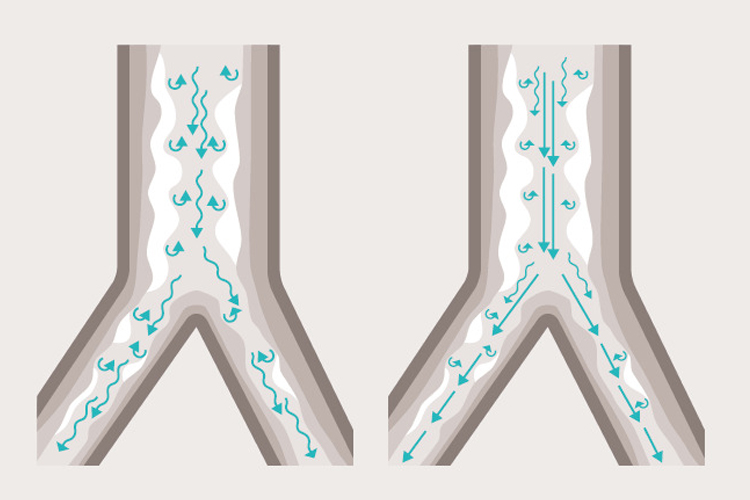
How Heliox therapy promotes better laminar flow with less turbulence
The illustration above shows how Heliox therapy (right) helps reduce airway pressure due to turbulence and blockage in a typical asthma patient. This low-density gas mix can be used for all types of patients above 3 kg. It is especially well suited to reduce the work of breathing (WoB) of patients with obstructed airways, such as those with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).[3],[4]

Safe, reliable and easy to use
When switching gas from air and O2 to Heliox and back, volume and CO2 monitoring as well as flow delivery are adjusted automatically by the ventilator’s Automatic Gas Identification. Heliox delivery is confirmed by the presence of the “HeO2” symbol on the screen. O2 concentration is easily adjusted between 21% – 100% and information texts facilitate Heliox administration in every mode.

High quality consumables
We offer an extensive range of readily available consumables designed for the highest possible patient safety and ease of use – all to help secure your everyday operations.
Smart fleet management
The Servo family of ventilators share the design, many components and come with the same easy-access service structure and interface.
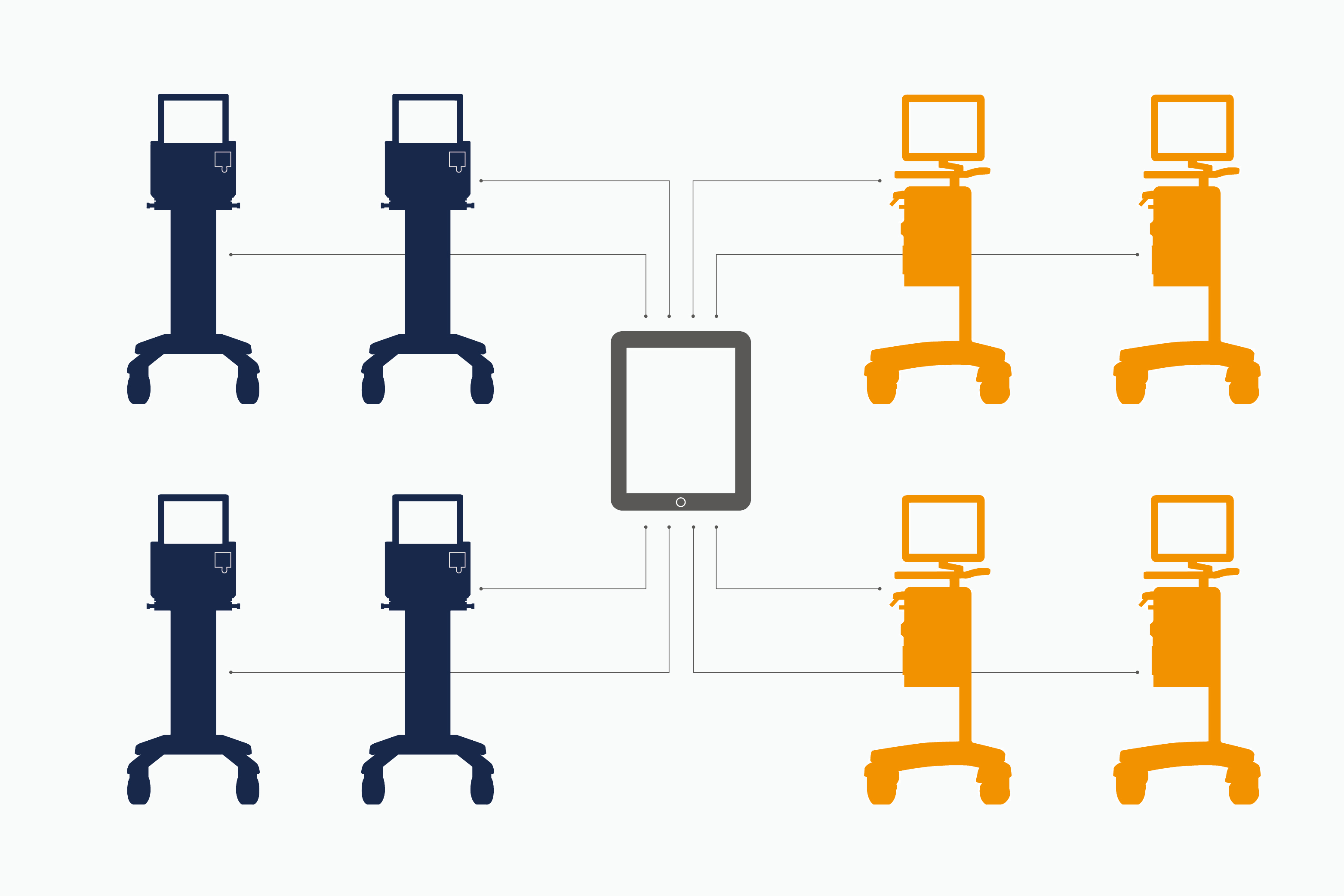
Connected to your data
MSync helps you to connect your Servo fleet to your patient monitor, HIS or patient data management system (PDMS). Clinical and patient data is transferred in real time to support clinical decision-making.

Maximum uptime
Optimizing your equipment's services is often an untapped opportunity. Our Getinge Care service offering will ensure that your equipment always performs at peak levels allowing you to focus on what’s important - saving lives.
Your environment. Your ventilator.
Your environment. Your ventilator.
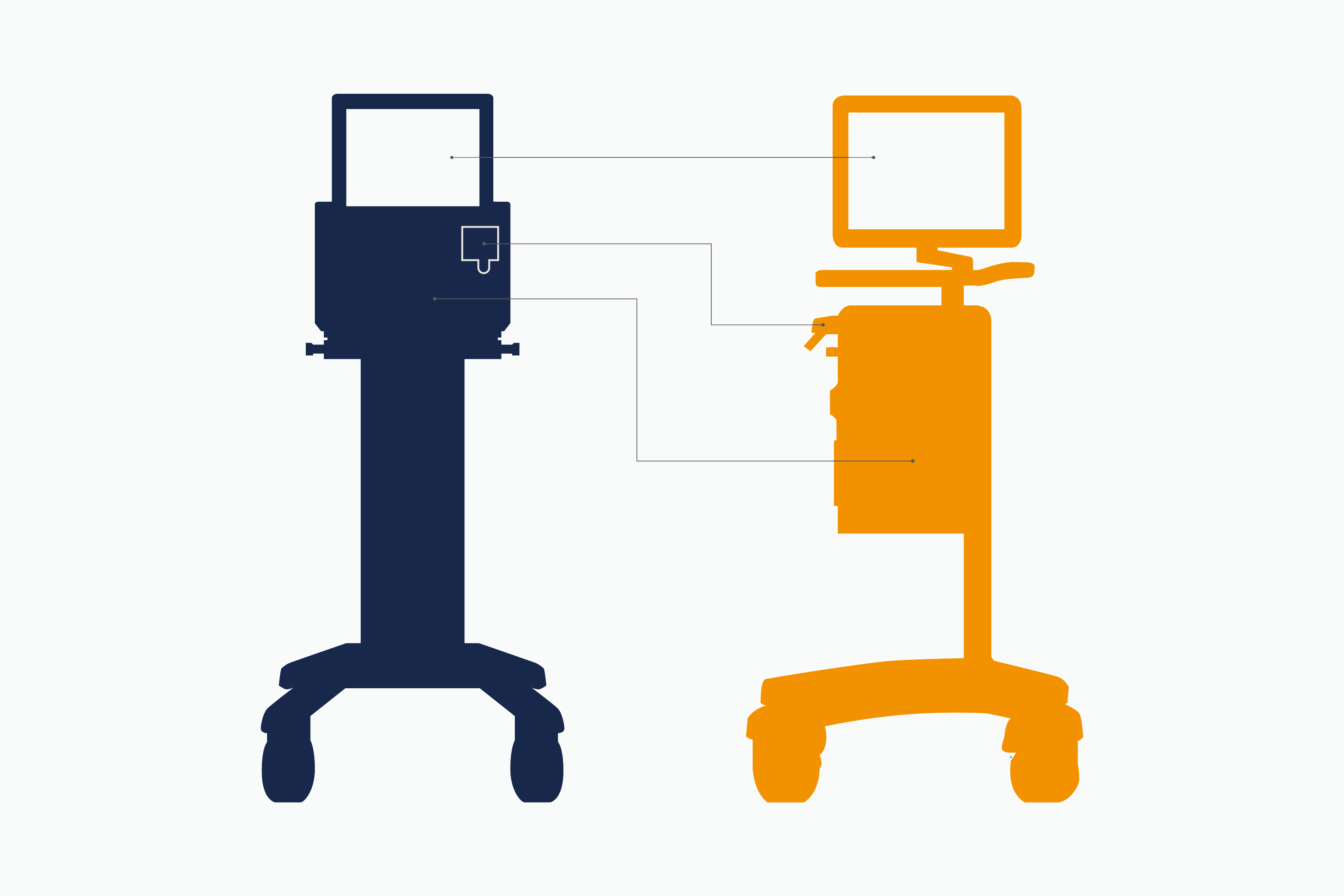
Shows safe distance to the MR scanner and alerts if too close.
Locks all wheels simultaneously once your hand leaves the handle.
Patient tubing connections and rotatable screen eases placement on either side of the MR table.
Let you see vital parameters at a glance from the control room and alerts of any deviation from set targets.
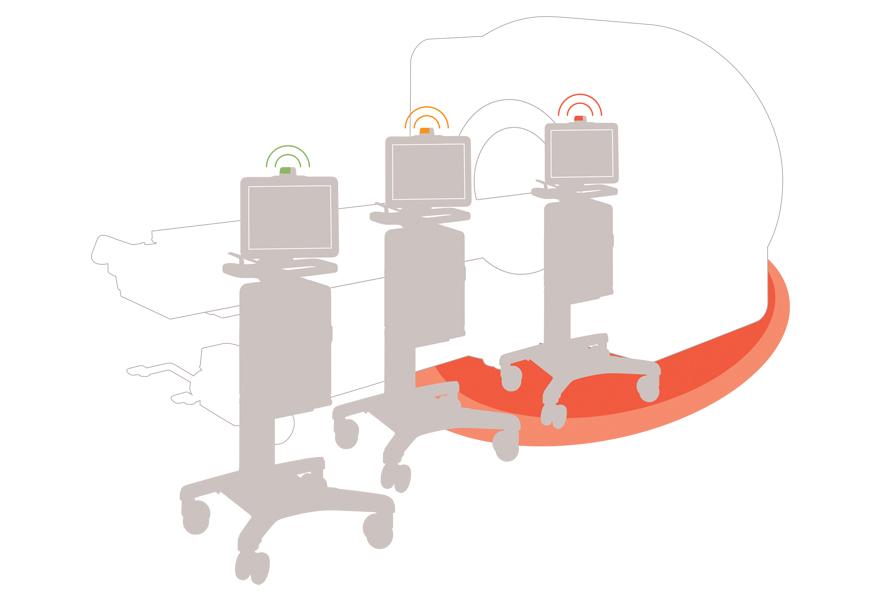
Put your mind at rest
The magnetic field is strong in the MR room. This is when the magnetic field indicator can help you with positioning. It guides you to a safe position with visual and audible alerts. Green means the ventilator system performs according to specifications. Yellow and red indicates you have gone too close to the MR Scanner.

In good hands
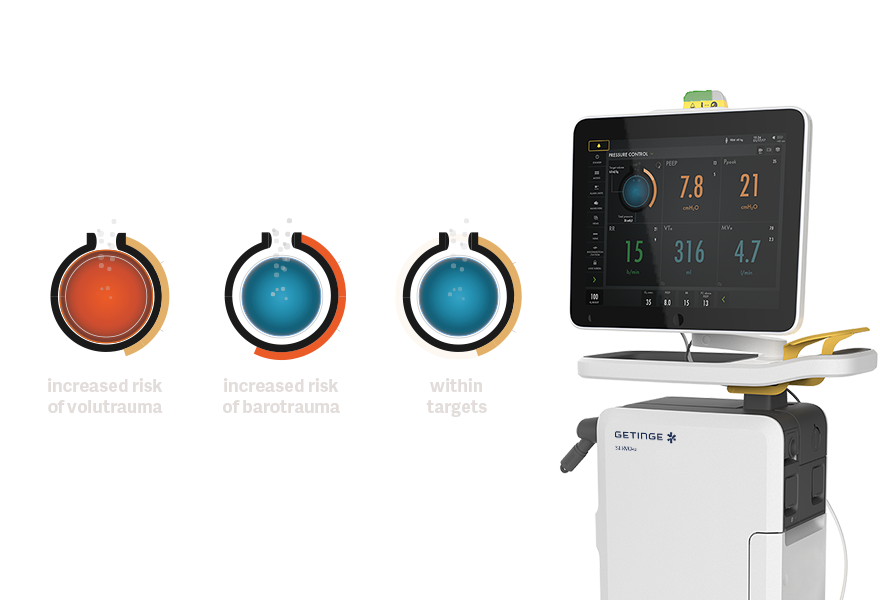
Servo Compass visualizes when driving pressure or tidal volume per kilogram of predicted bodyweight is off target and when adjustments are needed.
Precisely calculated dynamic compliance and Stress Index complete the picture, helping you detect changes in lung volume and verify over-distension [1] [2].
Marketing Sales - Sales Flyer
-
Expand the performance of your flexible Servo-u with additional functionalities and features allowing you to adapt more easily to your ever-changing clinical needs.
Marketing Sales - Brochures
-
The physiological challenges of mechanical ventilation requires a powerful toolkit, offering the right protection for each patient at the right time.
-
Achieve faster personalized weaning with lung and diaphragm-protective ventilation.
-
Help patients suffering from obstructive lung diseases, such as asthma, bronchiolitis, and COPD, breathe easier where additional targeted support may be required.
-
Protect your Getinge device and optimize the clinical workflow with Getinge high quality consumables.
Marketing Sales - Data Sheet
-
Servo-u MR technical specifications and information on intended use, clinical benefits, functionality, user interface, power supply, gas supply, weights and dimensions.